There is no an product in your account
please add some product to cart.
EXPERTS PREDICT: Fatty Liver Disease will affect 90 million people in 2017
Posted by John Coppola on 17 Feb, 18
THIN PEOPLE CAN HAVE DIABETES, TOO!
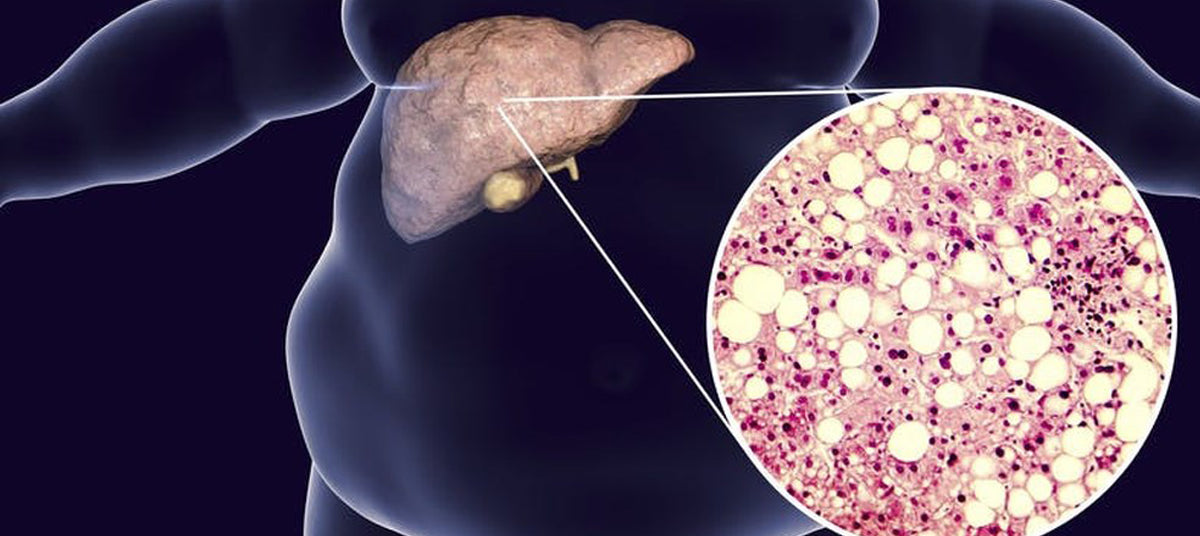
Throughout the U.S., U.K., and Australia, more and more cases of liver disease are arising in the absence of alcohol abuse. Decades ago, we only saw conditions like Fatty Liver Disease and cirrhosis occur as a direct result of excessive alcohol indulgence, however, this trend has changed in the current day. Today, more and more adults and children are being diagnosed with NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD).
NAFLD is a medical condition that is characterized by an excessive accumulation of fats, within liver cells. This means normal, healthy liver tissue becomes partly replaced with fatty tissue. The fat starts to invade the liver, gradually infiltrating the healthy liver areas, decreasing the amount of healthy active liver tissue.
While it’s normal for your liver to contain some fat, accumulations of more than 5 percent to 10 percent of your liver’s weight are problematic.
70 million Americans have fatty liver disease and don’t even know it.

Liver Function
The liver is one of the hardest-working organs in the body, working tirelessly day in and day out. So here’s what your liver does, in a nutshell. Your liver regulates most chemical levels in the blood and excretes bile. Bile is necessary to break down fats. All of the blood leaving the stomach and intestines must pass through the liver for filtering. It’s the liver’s responsibility to detoxify this blood.
Here are several other important functions of the liver:
- Detoxifies chemicals and metabolizes (breaks down) drugs.
- Manufactures proteins important for the regulation of blood clotting
- Breaks down excess hormones circulating in bloodstream
- Produces cholesterol (necessary for vitamin D and hormone production and for healthy nerves)
- Stores and releases glucose, as needed
- Stores iron
- Converts harmful ammonia to urea (urea is an end product of protein metabolism that gets excreted in the urine)
- Clears the blood of alcohol, medications, drugs and other harmful chemicals
- Produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream
- Clears and removes bilirubin (excessive buildup causes jaundice -yellowing of skin and eyes)
It’s the liver’s responsibility to process (store) nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals and iron, so they’re more efficiently absorbed.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFLD) has become increasingly common in the United States and Western Europe as weight gain, obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes and metabolic syndrome have risen in epidemic proportions. It is now the most common cause of liver disorders in the United States and other Western industrialized countries, such as Australia and the United Kingdom. It’s estimated that 1 in 5 people (25%) throughout these regions have NAFLD.
Although research has shown that NAFLD is most commonly caused by excess weight & obesity, metabolic syndrome and diabetes, studies have also revealed that the excessive use of prescribed medications and pain killers (or the toxicity of these) can lead to fatty liver disease, as well.
Liver Disease Symptoms

A non-alcoholic fatty liver is often referred to as a ‘Silent Disease’. Initially there may be no symptoms, meaning, you can live with the condition for many years, even decades, and not realize it. Over time, however, some signs may begin to surface.
These symptoms include:
- feeling tired
- fatigue
- weight loss
- loss of appetite
- weakness
- nausea
- confusion
- trouble concentrating
- pain in the center or right upper part of belly
- enlarged liver
- bloating and gas
- dark urine
- bruising easily
- sweating, excessively
- constipation
- dry and dark patches on neck and under arms
Over time, fatty liver disease can lead to cirrhosis of the liver. This occurs when scar tissue develops in the liver, preventing the liver from functioning properly. The scar tissue blocks the flow of blood through the liver and slows the processing of nutrients, hormones, drugs and naturally produced toxins, as well as the production of proteins and other substances made by the liver. Symptoms of cirrhosis are severe and include the buildup of fluid in the body (especially the abdominal cavity called ascites), muscle weakness, internal bleeding, yellowing of the skin and eyes, and liver failure.
Diagnosis of a Fatty Liver:
The best way to diagnose a fatty liver is with an abdominal ultrasound or a biopsy, although an ultrasound is far less invasive. Often, people with NAFLD will not have elevated liver enzymes, so the blood tests may look normal. Elevated liver enzymes however, do indicate that you have inflammation of the liver which may be do to NAFLD or a more serious condition called NASH.
Root Causes & Risk Factors of Liver Disease
There are a number of risk factors that increase your chances of having NAFLD:
- Obesity
- Gastric bypass surgery
- High cholesterol
- High levels of triglycerides in the blood
- Type 2 diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome
- Medications
- Sleep apnea
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
- Underactive pituitary gland (hypopituitarism)
- Hemachromatosis (excess iron accumulation)
A 2006 review published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology states that NAFLD is a common finding among patients undergoing bariatric surgery, with an occurrence ranging between 84 percent to 96 percent. The review also noted that the disease seems to be most common among men, and it increases with menopause in women.
Foods That Cause Fatty Liver Disease

High-Carbohydrate & Refined Foods
Foods such as bread, rice, and corn should be avoided. All white bread and carbs should be eliminated or significantly, reduced from your diet, and even whole grains should be consumed in moderation (because grains convert to sugar). All refined When we consume too many refined carbohydrates, insulin levels spike, and insulin sensitivity is a major factor in the cause of liver disease.
Sugary Drinks
Sports drinks (Gatorade/powerade), soda, energy drinks and fruit juices are full of sugar and artificial sweeteners. This sugar that enters your body causes fatty liver disease. The average 12-ounce can of soda, for example, has 10 teaspoons of sugar! Your body isn’t able to break down the amount of sugar that most Americans consume every day, and it’s impacting the liver, big time.
The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends no more than 6 tsp (25g) of sugar per day for women and 9 tsp (38g) per day for men. A child’s sugar intake should not exceed 3 tsp per day.
The average person consumes 20 tsp or more of sugar per day – equating to 66 pounds and more of sugar per year.
According to a study conducted at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, sugars, particularly fructose, are suspected to contribute to the development of NAFLD and its progression. Fructose has been shown in research to do extensive damage to liver cells. There have also been substantial links between increased fructose consumption and obesity, dyslipidemia and insulin resistance.
Processed Foods
Hydrogenated oils, refined sugar, convenience foods and lunch meats are notoriously toxic to your system. Nitrates and nitrites, for example, are commonly found in processed foods and lunch meat, and they have been linked to serious conditions, including cancer. The high fructose corn syrup found in our processed foods is the single biggest cause of fatty liver; you must stay away from these products in order to heal liver disease.
Foods That Improve Fatty Liver Disease
A review published in the European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry states that natural enzymes found in vegetables, as well as fruits, plant extracts and herbs, have been traditionally used for treating liver diseases. It’s incredibly important to add vegetables to your everyday diet.
An easy way to do this is by juicing vegetables for near-perfect health. With impaired liver function, juicing vegetables has the added benefit of making the vegetables easier to digest and more readily available for absorption. Vegetables ideal for a liver detox include kale, cabbage, lettuce, cauliflower, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, asparagus, beets and celery.

Beets
Beets naturally cleanse and purify the blood, which boosts liver function and nutrient production in your body. Beets are also high in antioxidants, folate, iron, fiber and betaine (a natural digestive enzyme). Beets go great in juicing recipes and thrown into smoothies (a little goes a long way). Shred some beets and throw on your salads, daily.

Broccoli
Broccoli and other members of the cruciferous family (brussel sprouts, cauliflower, arugula, cabbage, collard greens, kale, bok choy) are high in fiber and glucosinolates, which help the liver naturally cleanse the body of carcinogens and other toxins.

Ginger Root
Ginger has powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, especially necessary with a dysfunctional liver due to NAFLD. Ginger has also been found to drastically lower blood sugar levels. Elevated glucose and insulin resistance are 2 key factors in the development of a fatty liver. Make ginger tea by boiling ginger slices in green tea or water. You can also add ginger to a stir-fry, salad or smoothie.

Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes, along with carrots, butternut squash and pumpkin) are rich in beta-carotene, a natural anti-inflammatory. A deficiency of potassium can disrupt liver function. Sweet potatoes, naturally high in potassium, are beneficial because they help support liver function. One sweet potato contains nearly 700 milligrams of potassium! It’s also rich with vitamins B6, C, D, magnesium and iron. Sweet potatoes are easy to eat because they’re naturally sweet, and the sugars are slowly released into the bloodstream through the liver, so it won’t cause a spike in blood sugar.

Lemons
Lemons are great for your liver. They provide a wealth of antioxidants and help your liver produce more enzymes giving you more energy and help with digestion.. Lemons are also naturally high in electrolytes. Although lemons are acidic, once they enter the body they become alkalinizing, which helps neutralize toxins, excrete wastes. Juice 1 fresh lemon, daily and drink-undiluted on an empty stomach every morning.

Bananas
Containing 470 milligrams of potassium, banana nutrition is also great for cleansing the liver and overcoming low potassium levels; plus, bananas assist in digestion and help release toxins and heavy metals from the body. A great way to decrease the liver’s burden.

Garlic,whole cloves
Garlic is rich in allicin and selenium, two powerhouse nutrients for your liver. They act in cleansing and in nourishing the entire body, especially the blood. Selenium is a naturally detoxifying mineral and allicin helps ward off immune system invaders, which helps lighten the load on your liver. Garlic also activates enzymes in the liver which help with overall digestion and flushing out toxins. Use whole garlic cloves as the best option, instead of processed minced garlic or powder.

Leafy Greens
The nutritional all-star ingredients for just about every health issue are leafy greens. Spinach, kale, chard, romaine, arugula, and collards are all some of the most nutrient dense leafy greens to enjoy. They’re packed with chlorophyll, which assists in liver function by purifying the blood, alleviating toxins, decreasing inflammation and promotes wound healing. Chlorophyll is also amazing at neutralizing heavy metals, toxic chemicals, and even pesticides that burden the liver.
Supplements That Improve Fatty Liver Disease

Dandelion Root
The vitamins and nutrients present in dandelions help cleanse our livers and keep them working properly. Dandelions also aid our digestive system by maintaining the proper flow of bile. They’re natural diuretics and allow the liver to eliminate toxins quickly. Dandelion tea or stems are also high in vitamin C, which helps with mineral absorption, reduces inflammation and prevents the development of disease.

Milk Thistle
As a liver support and aid, milk thistle is a powerful detoxifier. It helps rebuild liver cells while removing toxins from the body that are processed through the liver. According to a study published in Digestive Diseases and Sciences, milk thistle has the power to improve mortality in patients with liver failure; it’s able to naturally reverse the harmful effects of alcohol consumption, pesticides in our food supply, heavy metals in our water supply, pollution in the air that we breathe in and even poisons.
According to a 2010 study, milk thistle benefits help treat alcoholic liver disease, acute and chronic viral hepatitis, and toxin-induced liver diseases.

Vitamin D
Recent studies have indicated that deficiencies in vitamin D can result in Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Vitamin D deficiency was shown to cause severe degrees of NAFLD along with liver inflammation and liver fibrosis (hardening). This research also revealed that vitamin D deficiencies also resulted in insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. All of these factors play a significant role in the development of peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage).
Optimum vitamin D levels should be between 70-100 ng/ml.

Curcumin
Curcumin, the active component of turmeric is arguably the most powerful herb on the planet at fighting and potentially reversing disease. Currently there have been over 6,000 peer-reviewed published articles proving the health benefits. Studies have also shown that curcumin may prevent the progression of fatty liver disease and reduces inflammation of the liver and body.

Black Seed Oil
This amazing oil can greatly speed the healing process for people with fatty liver disease. A study published in the European Review for Medical and Pharmaceutical Sciences measured black seed oil’s ability to inhibit liver oxidative stress markers. The results of the study indicated that black seed oil benefits liver disease patients because it’s able to reduce the complications and progression of fatty liver disease.
The best thing you can do to treat fatty liver disease is maintain a healthy diet. Many people with fatty liver disease are overweight and malnourished. A healthy diet that provides the vitamins and nutrients that your body needs to function is very important.
The number one treatment of fatty liver disease is weight loss and a healthy diet. It’s essential that you eat a well-balanced diet that is predominately plant-based; plus, you should exercise regularly — shoot for doing physical activity for at least 30 minutes a day, even if it’s taking a walk.
What Do Peripheral Neuropathy and Fatty Liver Disease Have In Common?
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is considered the most common liver disorder in the Western world. It’s recognized as one of the most common forms of chronic liver disease across the globe.

A study published in the Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology (2003) reported a link between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and peripheral neuropathy. The research revealed that 73% of people with NAFLD would develop peripheral nerve damage leading to the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy.
As if the development of peripheral neuropathy isn’t bad enough, science shows that the longer you have NAFLD, the more likely it is to progress into liver fibrosis (accumulation of abnormal fibrous tissue), cirrhosis (accumulation of scar tissue in the liver) and NASH (severe liver inflammation and cell damage).
Although, NAFLD is most likely to happen in people who are overweight with metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes, recently there are more and more cases of children with NAFLD. This is a direct result of the standard American diet. Pediatric NAFLD have been reported in children as young as 3 years old.
If you have been diagnosed with NAFLD or are overweight, suffer from metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance or diabetes, it’s important to take action. The good news is – The liver is the only organ capable of fully regenerating itself. As long as you have at least 15% of your liver that is working and functional, your body can repair and regenerate your liver.
 This blog has been provided by Dr. John Coppola, D.C. and Dr. Valerie Monteiro, D.C. Dr. Coppola and Dr. Monteiro are the founders of the San Antonio Neuropathy Center, and Precision Sport & Spine. They are the leading experts in the field of neuropathy and specifically drug free nerve repair. They are the authors of the critically acclaimed book "Defeat Neuropathy Now .... In Spite of Your Doctor. The doctors have over 25 years of clinical experience.
This blog has been provided by Dr. John Coppola, D.C. and Dr. Valerie Monteiro, D.C. Dr. Coppola and Dr. Monteiro are the founders of the San Antonio Neuropathy Center, and Precision Sport & Spine. They are the leading experts in the field of neuropathy and specifically drug free nerve repair. They are the authors of the critically acclaimed book "Defeat Neuropathy Now .... In Spite of Your Doctor. The doctors have over 25 years of clinical experience.
If you would like to reach the doctors regarding a specific health problem, you may email them at info@bodiesrebuilt.com.
- Bedogni G, Miglioli L, Masutti F, Tiribelli C, Marchesini G, Bellentani S. Prevalence of and risk factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the Dionysos nutrition and liver study. Hepatology. 2005;42:44–52. [PubMed]
- Adams LA, Lymp JF, Sauver J, St, et al. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:113–121. [PubMed]
Sourced through Scoop.it from: draxe.com